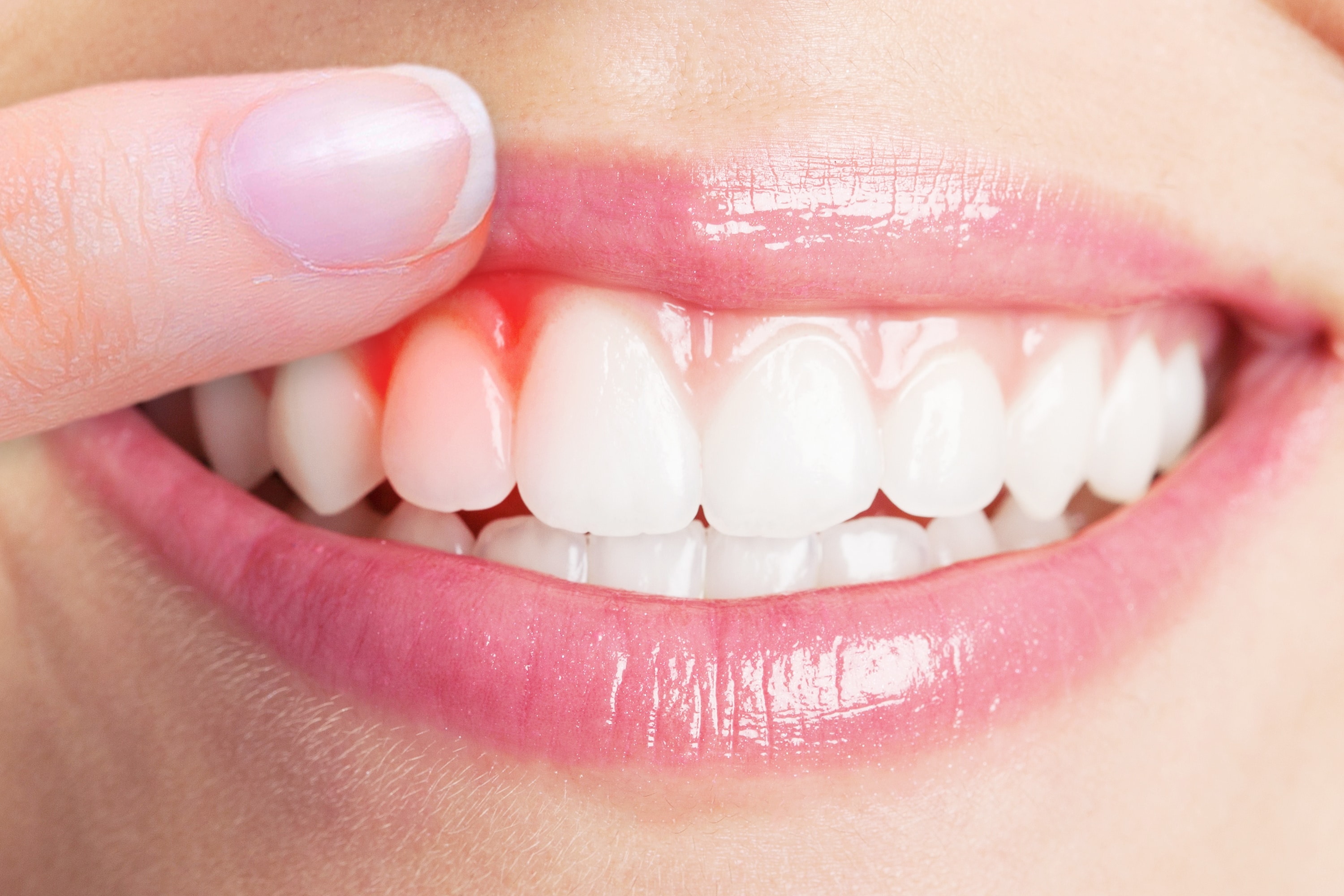

Gum Treatment
Gum disease is where the gums become swollen, sore or infected. The gums may bleed during tooth brushing and gum disease may cause bad breath. Gum disease is also called gingivitis or periodontal disease.
Periodontitis or pyorrhea is a set of inflammatory diseases affecting the tissues that surround and support the teeth. Periodontitis involves progressive loss of the alveolar bone around the teeth, and if left untreated, can lead to the loosening and subsequent loss of teeth. Periodontitis is caused by microorganisms that adhere to and grow on the tooth's surfaces, along with an over-aggressive immune response against these microorganisms.
A diagnosis of periodontitis is established by inspecting the soft gum tissues around the teeth with a probe (i.e., a clinical examination) and by evaluating the patient's X-ray films (i.e. a radiographic examination), to determine the amount of bone loss around the teeth.
- Redness or bleeding of gums while brushing teeth
- Gum swelling that recurs
- Spitting out blood after brushing teeth
- bad breath, and a persistent metallic taste in the mouth
- Loose teeth
- Gums that have pulled away from the teeth
- Pus between your teeth and gums
Signs and symptoms
In the early stages, periodontitis has very few symptoms; and in many individuals the disease has progressed significantly before they seek treatment. Symptoms may include:
Treatments for gum disease
The best treatment for gum disease is good oral hygiene, with regular tooth brushing, flossing and dental check-ups. In some cases, oral surgery or procedures will be recommended for severe cases of gum disease
Non-surgical treatments for gum disease
- Scaling and Root Planning: Manually removing the plaque and tarter from the root surfacrs of your teeth below the gums.
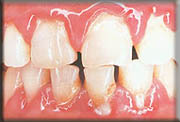
Before
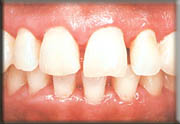
After
(Scaling and Root Planning)
- Antibiotics: Because bacteria cause periodontitis antibiotics may be prescribed as pills or as an Antibiotic fiber. The fibers are used in conjunction with scaling and root planing. They are placed directly into the pockets and are removed within 7-10 days later. Antibacterial mouth rinses may also be recommended to help plaque control.
- Splinting: This technique attaches weak teeth together, combining them into a stronger single unit, making them more stable and offering more comfortable chewing.
- Bite correction: An imbalanced bite may accelerate bone destruction. Your teeth may be adjusted for proper and better function. A Bite-guard (removable retainer fitting over teeth) may be required to protect teeth surfaces and relax tense muscles.
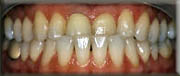
Before
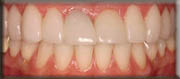
After
(Bite correction)
Surgical treatments for gum disease
- Flap Surgery/pocket reduction surgery: During this procedure the gums are lifted back and the tarter is removed. In some cases, irregular surfaces of the damaged bone are smoothed to limit areas where disease-causing bacteria can grow. The gums are then placed so that the tissue fits snugly around the tooth. This method reduces the size of the space between the gum and tooth, thereby decreasing the areas where harmful bacteria can grow and decreasing the chance of serious health problems associated with periodontal disease.
-
Bone Grafts: Today, our Periodontist , are often able to restore or regenerate missing bone and attachment around teeth subjected to long-standing periodontal disease. In addition, if you have lost a tooth due to trauma or disease, we can restore or regenerate bone prior to the placement of bridges or implants.
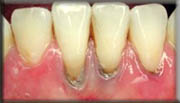
Before
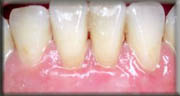
After
(Bone Grafting)
- Soft tissue grafts: This procedure reinforces thin gums or fills in places where gums have receded. Grafted tissue, most often taken from the roof of the mouth, is stitched in place, adding tissue to the affected area.
- Gingivectomy: This procedure is performed when excess amounts of gum growth around the teeth have occurred. This results in false pocket formation and the inability to keep them clean.